Memcached内存分配原理
Memcached采用的是Slab内存分配机制管理内存。它的基本原理是按照预先分配的大内存分成大小相等的slab(默认为1M),每个slab又分割成多个相同尺寸的块(chunk),并把尺寸相同的块组成slabclass,以提高内存请求分配效率和解决内存碎片问题。
slab
slab 源于Jeff Bonwick 为Solaris操作系统首次引入的一种内存处理机制,SLAB的设计理念是基于对象缓冲的,基本想法是避免重复大量的初始化和清理操作。slab主要可以用于频繁分配释放的内存对象,如果是采用系统自带的malloc/free系列函数, 反复地操作会造成大量内存碎片,且时间效率不高。
内存管理机制
- 内存分配机制:Slab Allocation
- 内存预分配,组织成不同尺寸的块,以适应不同大小的内存请求
- 避免大量的内存分配与释放(mallock,free)
- 减少内存碎片
- 数据过期机制:Lazy Expiration + LRU
- 不检查item对象是否超时,等待get时再行判断
- 删除对象时,不释放内存,将内存放入相应的空闲链表中
- 对象替换策略采用LRU算法
- 检索机制:Hash
- 提高检索效率
核心数据结构
基本概念
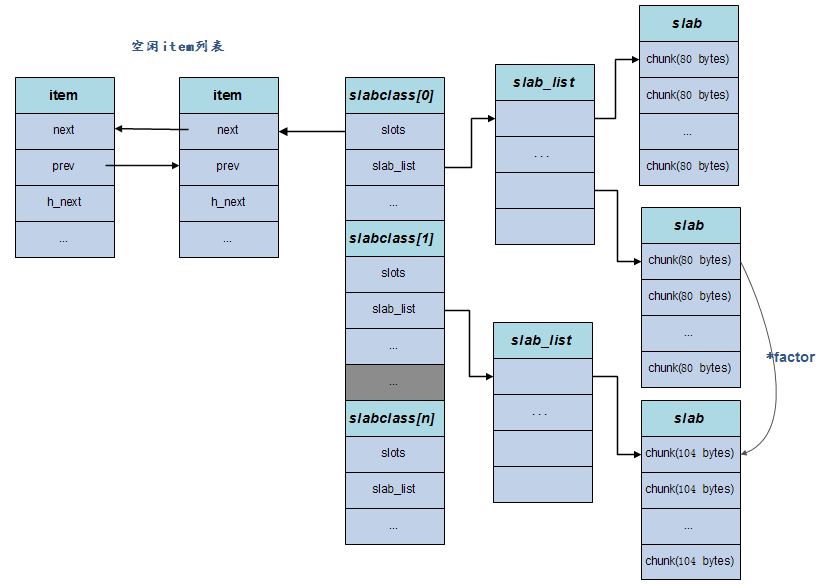
- slabclass: Memcached存在一个slabclass集合,每个slabclass提供固定大小的内存(chunk)分配,不同slabclass对外分配的内存大小也不一样。初始化的时候,会根据factor确定每个slabclass所要分配的内存大小。
- Item:存储项,存储一个具体的key-value结构,其空间来源于chunk。
- chunk : 实际用来存储数据的内存空间,chunk就是属于某个slabclass分配出去的固定大小内存。
- slab:一次申请内存的最小单位,默认是1MB,当一个slabclass没有内存可用时,需要向系统申请新的空间,这时候都是依照一 个slab的大小来申请的。当一个slab可用的chunk分配完后,可继续申请新的slab使用,若slab申请失败(mem_limit所限制),则slab Allocator管理机制通过LRU算法选择最近最小使用且合适的chunk返回,以存储新的数据。
Memcached预先将数据空间划分为一系列大小的slabclass,每个slabclass只负责一定大小范围内的数据存储, 即slabclass只存储大于其上一个slabclass中chunk的size并小于或者等于自己最大size的数据。
Memcached根据所收到数据的大小,选择最适合数据大小的slabclass,然后从空闲chunk列表取出一个chunk, 然后将数据缓存于其中。
slab是Memcached在收到内存不够的请求,并进行内存分配的单位。举例来说,slabclass[2]中所有的chunk空间都用完了,系统又要在slabclass[2]中申请一个chunk,这时就会向Memcached请求新的内存空间,Memcached就会f分配一个slab到slabclass[2],slab的默认大小是1M。 chunk是实际用来存储数据的内存空间。一个slab大小的内存可分割成 slab / chunksize 个chunk。
slabclass结构体
typedef struct {
unsigned int size; /* item的大小 */
unsigned int perslab; /* 每一个slab的item数量 */
void *slots; /* 空闲item(被回收的item)链表的指针 */
unsigned int sl_curr; /* 空闲item的总数量 */
unsigned int slabs; /* 在这个slabclass中已分配slab的数量 */
void **slab_list; /* slab数组 */
unsigned int list_size; /* 数组的大小 */
unsigned int killing; /* index+1 of dying slab, or zero if none */
size_t requested; /* 被访问到的字节数 */
} slabclass_t;
item结构体
/**
* Memcached存储item的结构体
*/
typedef struct _stritem {
struct _stritem *next; /* 双向链表 */
struct _stritem *prev;
struct _stritem *h_next; /* 指向hash值相同的下一个元素 */
rel_time_t time; /* 最近访问的时间 */
rel_time_t exptime; /* 过期时间 */
int nbytes; /* 数据大小 */
unsigned short refcount; /* 被引用数 */
uint8_t nsuffix; /* 后缀长度 */
uint8_t it_flags; /* ITEM_* above */
uint8_t slabs_clsid;/* 此item所属哪个slabclass */
uint8_t nkey; /* 键的长度 */
/* this odd type prevents type-punning issues when we do
* the little shuffle to save space when not using CAS. */
union {
uint64_t cas;
char end;
} data[];
/* if it_flags & ITEM_CAS we have 8 bytes CAS */
/* then null-terminated key */
/* then " flags length\r\n" (no terminating null) */
/* then data with terminating \r\n (no terminating null; it's binary!) */
} item;
slab.c核心代码解析
初始化slabclass
/**
* 初始化slabclass数组
*
* 1. 若预分配(preallock = true),则分配一大段内存limit,并初始化
* 2. 初始化slabclass数组
* 包括块大小(size: item结构体+数据),每个slab能包含多少个块(perslab),所分配的chunk是字节对齐的
* 默认的slab大小为1M, slab >= size * perslab. 所以每个slab中可能存在尾部碎片
* 3. 若预分配,slab初始化, 具体看slabs_preallocate()的分析
*
* limit等价于 –m指定的内存分配最大值,factor等价于-f参数, preallocate等价于-L参数
* 如果设置了-L参数,则尝试一次性申请maxbytes大小的内存,指针保存到全局的mem_base变量里,未来所有内存申请实际上是从这块内存区域中分配的
*/
void slabs_init(const size_t limit, const double factor, const bool prealloc) {
int i = POWER_SMALLEST - 1; // POWER_SMALLEST : slabclass数组的最小下标, 默认为1
unsigned int size = sizeof(item) + settings.chunk_size;
mem_limit = limit;
if (prealloc) {
/* 用malloc分配一块大内存 */
mem_base = malloc(mem_limit);
if (mem_base != NULL) {
mem_current = mem_base;
mem_avail = mem_limit;
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Warning: Failed to allocate requested memory in"
" one large chunk.\nWill allocate in smaller chunks\n");
}
}
memset(slabclass, 0, sizeof(slabclass));
while (++i < POWER_LARGEST && size <= settings.item_size_max / factor) {
/* Make sure items are always n-byte aligned */
if (size % CHUNK_ALIGN_BYTES)
size += CHUNK_ALIGN_BYTES - (size % CHUNK_ALIGN_BYTES); //字节对齐
slabclass[i].size = size;
slabclass[i].perslab = settings.item_size_max / slabclass[i].size;
size *= factor;
if (settings.verbose > 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "slab class %3d: chunk size %9u perslab %7u\n",
i, slabclass[i].size, slabclass[i].perslab);
}
}
power_largest = i;
slabclass[power_largest].size = settings.item_size_max;
slabclass[power_largest].perslab = 1;
if (settings.verbose > 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "slab class %3d: chunk size %9u perslab %7u\n",
i, slabclass[i].size, slabclass[i].perslab);
}
/* for the test suite: faking of how much we've already malloc'd */
{
char *t_initial_malloc = getenv("T_MEMD_INITIAL_MALLOC");
if (t_initial_malloc) {
mem_malloced =
(size_t)atol(t_initial_malloc);
}
}
if (prealloc) {
/**
* m = min(maxslabs, POWER_LARGEST)
* 为slabclass[POWER_SMALLEST.. m]数组的每一项分配一个slab的空间,并划分成chunk
*/
slabs_preallocate(power_largest);
}
}
确认slabclassID
对于不同大小的数据,首先要确定这些数据需要在哪个slabclass里存放,轮询每个slabclass的chunk,返回此slabclass的id
/**
* 给定一个对象大小的字节数,返回容纳该对象的chunk属于哪个slabclass
*
*/
unsigned int slabs_clsid(const size_t size) {
int res = POWER_SMALLEST;
if (size == 0)
return 0;
while (size > slabclass[res].size)
if (res++ == power_largest) /* won't fit in the biggest slab */
return 0;
return res;
}
Memcached分配内存的好处是不会存在内存碎片,但是坏处也很明显,就是内存的浪费。如:slabclass[1]中的chunk大小为80字节,slabclass[2]中的chunk大小为104字节,对于需要请求81字节的chunk,则会浪费23字节的空间。
申请chunk
内存申请过程涉及到两个函数,一个函数用于申请新的slab page,一个函数用于从slabclass里分配空闲的chunk, 当无法从do_slabs_newslab()中分配出新的空间,导致do_slabs_alloc()也只能返回NULL的时候,Memcached进行LRU淘汰。
/**
* 在slabclass[id]中,分配一个size大小的item。失败返回0,成功返回item的地址
*
* 1. id校验
* 2. 若slabclass[id]中没有空闲的item,则请求分配一个新的slab,若请求失败,则返回0
* 3. 返回slots链表中的第一个元素,slabclass[id]的空闲item数减一
*/
static void *do_slabs_alloc(const size_t size, unsigned int id) {
slabclass_t *p;
void *ret = NULL;
item *it = NULL;
// id校验
if (id < POWER_SMALLEST || id > power_largest) {
MEMCACHED_SLABS_ALLOCATE_FAILED(size, 0);
return NULL;
}
p = &slabclass[id];
/* 当前slabclass[id]的可用chunk数为0, 或者slots的第一个元素的slabclass Id为0
* 不太理解后者,slabclass id为0表示无效啊,那什么情况下又是赋予0的?
*/
assert(p->sl_curr == 0 || ((item *)p->slots)->slabs_clsid == 0);
/* fail unless we have space at the end of a recently allocated page,
we have something on our freelist, or we could allocate a new page */
if (! (p->sl_curr != 0 || do_slabs_newslab(id) != 0)) {
/* We don't have more memory available */
ret = NULL;
} else if (p->sl_curr != 0) {
/* return off our freelist */
it = (item *)p->slots;
p->slots = it->next;
if (it->next) it->next->prev = 0;
p->sl_curr--;
ret = (void *)it;
}
if (ret) {
p->requested += size;
MEMCACHED_SLABS_ALLOCATE(size, id, p->size, ret);
} else {
MEMCACHED_SLABS_ALLOCATE_FAILED(size, id);
}
return ret;
}
/**
* 为slabclass[id]分配一个新的slab,成功返回1,否则返回0
*
* 1. 确定slab的长度len
* 2. 分配len大小的内存(预分配的内存中划分或者调malloc()分配)
* 3. 把所分配的内存初始化成item链表,链接到slabclass[id]的slot中
* 4. slabclass[i]属性的更新:slabs数增1
* 5. 已分配内存数的更新
*/
static int do_slabs_newslab(const unsigned int id) {
slabclass_t *p = &slabclass[id];
int len = settings.slab_reassign ? settings.item_size_max
: p->size * p->perslab;
char *ptr;
if ((mem_limit && mem_malloced + len > mem_limit && p->slabs > 0) ||
(grow_slab_list(id) == 0) ||
((ptr = memory_allocate((size_t)len)) == 0)) {
MEMCACHED_SLABS_SLABCLASS_ALLOCATE_FAILED(id);
return 0;
}
memset(ptr, 0, (size_t)len);
split_slab_page_into_freelist(ptr, id);
p->slab_list[p->slabs++] = ptr;
mem_malloced += len;
MEMCACHED_SLABS_SLABCLASS_ALLOCATE(id);
return 1;
}
线程安全
Memcached中slabs_alloc()函数是do_slabs_alloc()函数线程安全版本。
/** 线程安全的do_slabs_alloc() */
void *slabs_alloc(size_t size, unsigned int id) {
void *ret;
pthread_mutex_lock(&slabs_lock);
ret = do_slabs_alloc(size, id);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&slabs_lock);
return ret;
} 相应地,do_slabs_free/stats等函数也有相应的线程安全版本
LRU
Memcached内部不会监视记录是否过期,而是在get时查看记录的时间戳,检查记录是否过期。 这种技术被称为lazy(惰性)expiration,因此,memcached不会在过期对象监视上耗费CPU时间。如果某一个item在Memcached里过期了,这个东西并不会被删除,而是客户端无法再看见该记录(invisible,透明), 其存储空间即可重复使用。一般情况下Memcached会优先使用已超时的记录的空间,但即使如此,也会发生追加新记录时空间不足的情况, 此时就要使用名为 Least Recently Used(LRU)机制来分配空间,从最近未被使用的记录中搜索,并将其空间分配给新的记录。
当无法从现有chunk中找到过期内容同时无法从class里继续分配新的chunk,这时候尝试LRU过程,先删过期内容,如果还无法分配,就开始删最近的内容。
- 每个slabclass对应一个item的双向链表,队头指向最近被访问的元素,队尾指向最老的元素。
- 当新的内存分配请求到来,且没有可用的slab可供分配时,触发LRU策略。
释放资源
无论是通过LRU策略还是通过其它主动淘汰策略,都需要标记refcount = 0(引用计数),然后才会通过do_slabs_free()释放资源,等待其它资源申请的时候使用。
/**
* 将ptr所指向的item链入slabclass[id]的slot链表中
*
*/
static void do_slabs_free(void *ptr, const size_t size, unsigned int id) {
slabclass_t *p;
item *it;
assert(((item *)ptr)->slabs_clsid == 0);
assert(id >= POWER_SMALLEST && id <= power_largest);
if (id < POWER_SMALLEST || id > power_largest)
return;
MEMCACHED_SLABS_FREE(size, id, ptr);
p = &slabclass[id];
it = (item *)ptr;
it->it_flags |= ITEM_SLABBED; // 设置item的标志
it->prev = 0;
it->next = p->slots;
if (it->next) it->next->prev = it;
p->slots = it;
p->sl_curr++; // chunk可用数增1
p->requested -= size;
return;
}
item.c核心代码解析
item空间分配
/**
* 根据item参数,分配item空间
*
* 1. 计算item所需空间大小
* 2. 计算此item属于哪个slabclass id
* 3. 快速检查在slabclass[id]所属的LRU队列中(从尾端开始)是否有过期的item
* 4. 对item初始化:item结构体属性,key,suffix,不包含value
*/
item *do_item_alloc(char *key, const size_t nkey, const int flags,
const rel_time_t exptime, const int nbytes,
const uint32_t cur_hv) {
uint8_t nsuffix;
item *it = NULL;
char suffix[40];
size_t ntotal = item_make_header(nkey + 1, flags, nbytes, suffix, &nsuffix);
if (settings.use_cas) {
ntotal += sizeof(uint64_t);
}
unsigned int id = slabs_clsid(ntotal);
if (id == 0)
return 0;
mutex_lock(&cache_lock);
/* do a quick check if we have any expired items in the tail.. */
int tries = 5;
int tried_alloc = 0;
item *search;
void *hold_lock = NULL;
rel_time_t oldest_live = settings.oldest_live;
search = tails[id];
/* We walk up *only* for locked items. Never searching for expired.
* Waste of CPU for almost all deployments */
/*
* 只搜索加锁的item项,而不搜索过期的item,因为那样会浪费很多CPU时间
*/
for (; tries > 0 && search != NULL; tries--, search=search->prev) {
uint32_t hv = hash(ITEM_key(search), search->nkey, 0);
/* Attempt to hash item lock the "search" item. If locked, no
* other callers can incr the refcount
*/
/* FIXME: I think we need to mask the hv here for comparison? */
if (hv != cur_hv && (hold_lock = item_trylock(hv)) == NULL)
continue;
/* Now see if the item is refcount locked */
if (refcount_incr(&search->refcount) != 2) {
refcount_decr(&search->refcount);
/* Old rare bug could cause a refcount leak. We haven't seen
* it in years, but we leave this code in to prevent failures
* just in case */
if (search->time + TAIL_REPAIR_TIME < current_time) {
itemstats[id].tailrepairs++;
search->refcount = 1;
do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hv);
}
if (hold_lock)
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
continue;
}
/* Expired or flushed */
if ((search->exptime != 0 && search->exptime < current_time)
|| (search->time <= oldest_live && oldest_live <= current_time)) {
itemstats[id].reclaimed++;
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_FETCHED) == 0) {
itemstats[id].expired_unfetched++;
}
it = search;
slabs_adjust_mem_requested(it->slabs_clsid, ITEM_ntotal(it), ntotal);
do_item_unlink_nolock(it, hv);
/* Initialize the item block: */
it->slabs_clsid = 0;
} else if ((it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id)) == NULL) {
tried_alloc = 1;
if (settings.evict_to_free == 0) {
itemstats[id].outofmemory++;
} else {
itemstats[id].evicted++;
itemstats[id].evicted_time = current_time - search->time;
if (search->exptime != 0)
itemstats[id].evicted_nonzero++;
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_FETCHED) == 0) {
itemstats[id].evicted_unfetched++;
}
it = search;
slabs_adjust_mem_requested(it->slabs_clsid, ITEM_ntotal(it), ntotal);
do_item_unlink_nolock(it, hv);
/* Initialize the item block: */
it->slabs_clsid = 0;
/* If we've just evicted an item, and the automover is set to
* angry bird mode, attempt to rip memory into this slab class.
* TODO: Move valid object detection into a function, and on a
* "successful" memory pull, look behind and see if the next alloc
* would be an eviction. Then kick off the slab mover before the
* eviction happens.
*/
if (settings.slab_automove == 2)
slabs_reassign(-1, id);
}
}
refcount_decr(&search->refcount);
/* If hash values were equal, we don't grab a second lock */
if (hold_lock)
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
break;
}
if (!tried_alloc && (tries == 0 || search == NULL))
it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id);
if (it == NULL) {
itemstats[id].outofmemory++;
mutex_unlock(&cache_lock);
return NULL;
}
assert(it->slabs_clsid == 0);
assert(it != heads[id]);
/* Item initialization can happen outside of the lock; the item's already
* been removed from the slab LRU.
*/
it->refcount = 1; /* the caller will have a reference */
mutex_unlock(&cache_lock);
it->next = it->prev = it->h_next = 0;
it->slabs_clsid = id;
DEBUG_REFCNT(it, '*');
it->it_flags = settings.use_cas ? ITEM_CAS : 0;
it->nkey = nkey;
it->nbytes = nbytes;
memcpy(ITEM_key(it), key, nkey);
it->exptime = exptime;
memcpy(ITEM_suffix(it), suffix, (size_t)nsuffix);
it->nsuffix = nsuffix;
return it;
}
item更新与替换
/**
* 更新item的时间,若item的时间相对于在当前时间的ITEM_UPDATE_INTERVAL范围之内,则不修改(效率的考虑)
*/
void do_item_update(item *it) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_UPDATE(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
if (it->time < current_time - ITEM_UPDATE_INTERVAL) {
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0);
mutex_lock(&cache_lock);
if ((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) != 0) {
item_unlink_q(it);
it->time = current_time;
item_link_q(it);
}
mutex_unlock(&cache_lock);
}
}
/**
* 用new_it替换it
* 这两个item的hashvalue相同?
*/
int do_item_replace(item *it, item *new_it, const uint32_t hv) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_REPLACE(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes,
ITEM_key(new_it), new_it->nkey, new_it->nbytes);
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0);
do_item_unlink(it, hv);
return do_item_link(new_it, hv);
}
item空间释放
/**
*
* 将item放入slabclass[id]的slot链表中
*
* 1. item属性校验
* 2. item的slabs_clsid属性修改
* 3. item空间“释放”
*/
void item_free(item *it) {
size_t ntotal = ITEM_ntotal(it);
unsigned int clsid;
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) == 0);
assert(it != heads[it->slabs_clsid]);
assert(it != tails[it->slabs_clsid]);
assert(it->refcount == 0);
/* so slab size changer can tell later if item is already free or not */
clsid = it->slabs_clsid;
it->slabs_clsid = 0;
DEBUG_REFCNT(it, 'F');
slabs_free(it, ntotal, clsid);
}
/**
* 如果item没有在其他地方引用,则把它归还到特定的slabclass中
*/
void do_item_remove(item *it) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_REMOVE(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0); // ITEM_SLABBED已经被删除后被标记。
if (refcount_decr(&it->refcount) == 0) {
item_free(it);
}
}
item的LRU队列和Hash
/**
* 将item添加至它所属LRU链表的头部
*/
static void item_link_q(item *it) { /* item is the new head */
item **head, **tail;
assert(it->slabs_clsid < LARGEST_ID);
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0);
head = &heads[it->slabs_clsid];
tail = &tails[it->slabs_clsid];
assert(it != *head);
assert((*head && *tail) || (*head == 0 && *tail == 0));
it->prev = 0;
it->next = *head;
if (it->next) it->next->prev = it;
*head = it;
if (*tail == 0) *tail = it;
sizes[it->slabs_clsid]++;
return;
}
/**
* 从LRU链表中移除item
* 注:并没有释放item的内存空间
*/
static void item_unlink_q(item *it) {
item **head, **tail;
assert(it->slabs_clsid < LARGEST_ID);
head = &heads[it->slabs_clsid];
tail = &tails[it->slabs_clsid];
if (*head == it) {
assert(it->prev == 0);
*head = it->next;
}
if (*tail == it) {
assert(it->next == 0);
*tail = it->prev;
}
assert(it->next != it);
assert(it->prev != it);
if (it->next) it->next->prev = it->prev;
if (it->prev) it->prev->next = it->next;
sizes[it->slabs_clsid]--;
return;
}
/**
* 将item关联到hash表中,并链入LRU链表中
*
* 1. item的flag,time属性的更新
* 2. 更新stats内容(全局资源需加锁)
* 3. 更新item的cas值
* 4. 将item关联到hash表中,并链入LRU链表中
* 5. 更新item的引用数
*/
int do_item_link(item *it, const uint32_t hv) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_LINK(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
assert((it->it_flags & (ITEM_LINKED|ITEM_SLABBED)) == 0);
mutex_lock(&cache_lock);
it->it_flags |= ITEM_LINKED;
it->time = current_time;
STATS_LOCK();
stats.curr_bytes += ITEM_ntotal(it);
stats.curr_items += 1;
stats.total_items += 1;
STATS_UNLOCK();
/* Allocate a new CAS ID on link. */
ITEM_set_cas(it, (settings.use_cas) ? get_cas_id() : 0);
assoc_insert(it, hv);
item_link_q(it);
refcount_incr(&it->refcount);
mutex_unlock(&cache_lock);
return 1;
}
/**
* 将item从hash表中和LRU链表中删除,把资源链如到特定的slabclass的slot中
*
* 1. item的flag属性的更新
* 2. 更新stats内容(全局资源需加锁)
* 3. 将item从hash表中和LRU链表中删除
* 4. 把资源链如到特定的slabclass的slot中
*/
void do_item_unlink(item *it, const uint32_t hv) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_UNLINK(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
mutex_lock(&cache_lock);
if ((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) != 0) {
it->it_flags &= ~ITEM_LINKED;
STATS_LOCK();
stats.curr_bytes -= ITEM_ntotal(it);
stats.curr_items -= 1;
STATS_UNLOCK();
assoc_delete(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, hv);
item_unlink_q(it);
do_item_remove(it);
}
mutex_unlock(&cache_lock);
}
存储分配的slab机制和hash表的检索相互透明,通过item实现两层的解耦。